Born - 19th June 1623
Parents - Etienne Pascal , Antoinette Begon
Pascal was a very enthusiastic and nerdy kid who started working on calculating machines, even when he was a teenager. After 3 years of tiresome research and making of 50 prototypes of his Pascal's calculator he at last built 20 finished machines of the later named Pascalines. At the age of 16 he wrote a significant treaty on the subject of Projective Geometry. And later followed Pierre De Fermant on probability theory and strongly supported the development of modern economic and social science. In 1946 he followed Galileo Galilei and Torricelli and did research against the theory of "Nature Abhors a Vaccum" proposed by one of Aristotle's followers. Then Pascal's research was at last accepted after many disputes. After the loss of his widower father in 1651 because of religious movements within Catholicism Pascal began writing influential works on philosophy and theology in the year 1654. The most famous of his philosophical works are "Lettres Provinciales and Pensees - which was his last incomplete work during his death period". One of his main service to mathematics was his discovery of "treaties on the Arithmetic Triangle" which is a convenient way of describing binomial coefficients through a tabular presentation which is now called Pascal's Triangle.
 |
| Blaise Pascal |
Pascal was a very enthusiastic and nerdy kid who started working on calculating machines, even when he was a teenager. After 3 years of tiresome research and making of 50 prototypes of his Pascal's calculator he at last built 20 finished machines of the later named Pascalines. At the age of 16 he wrote a significant treaty on the subject of Projective Geometry. And later followed Pierre De Fermant on probability theory and strongly supported the development of modern economic and social science. In 1946 he followed Galileo Galilei and Torricelli and did research against the theory of "Nature Abhors a Vaccum" proposed by one of Aristotle's followers. Then Pascal's research was at last accepted after many disputes. After the loss of his widower father in 1651 because of religious movements within Catholicism Pascal began writing influential works on philosophy and theology in the year 1654. The most famous of his philosophical works are "Lettres Provinciales and Pensees - which was his last incomplete work during his death period". One of his main service to mathematics was his discovery of "treaties on the Arithmetic Triangle" which is a convenient way of describing binomial coefficients through a tabular presentation which is now called Pascal's Triangle.
The Pascal Triangle (theoretical)
The number in the (m + 1)th row and (n + 1)th column are called tmn. Then tmn = tm–1,n + tm,n–1, for m = 0, 1, 2, ... and n = 0, 1, 2, ... The main conditions are tm,−1 = 0, t−1,n = 0 for m = 1, 2, 3, ... and n = 1, 2, 3, ... The generator t00 = 1. He then concludes with the proof,
In 1658 he wrote the cyloid and its uses in calculating the volume of solids. But on 19th August 1662 we sadly lost this nerdy youth.
To honor his scientific, mathematical, philosophical contributions to the world we have given the SI unit of a pressure his name (Pascal)
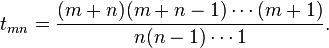

No comments:
Post a Comment